Bluetooth Mesh¶
Introduction to Mesh¶
Bluetooth Mesh is a new standard from Bluetooth SIG that was released in 2017. It enables many-to-many device communication (as opposed to point-to-point approach in BLE) and is optimised for large-scale networks like building automation or sensors network. It utilizes managed flood based approach where only mains-powered nodes relay messages making it very power efficient (battery powered low-power nodes that don’t relay messages can operate in mesh network for years).
Bluetooth Mesh is complementary to Bluetooth specification and requires features from 4.0 release only. This allows deployment of networks using hardware already available on the market.
Topology¶
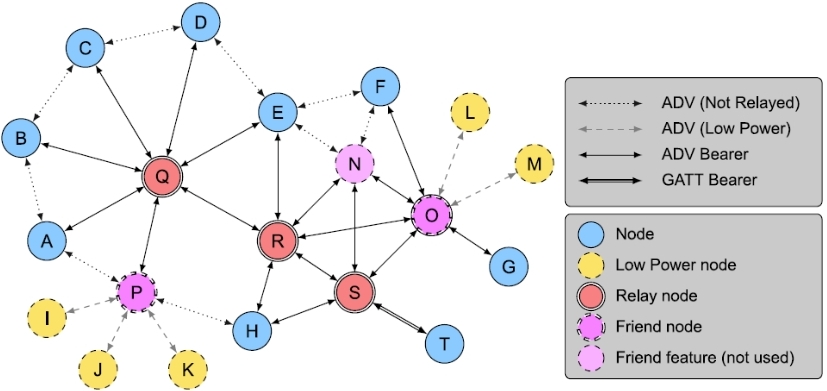
Bluetooth Mesh defines few features (roles) for devices in network. Those are:
Relay - receive and retransmit mesh messages over the advertising bearer to enable larger networks
Proxy - receive and retransmit mesh messages between GATT and advertising bearers.
Low Power - operate within a mesh network at significantly reduced receiver duty cycles only in conjunction with a node supporting the Friend feature
Friend - the ability to help a node supporting the Low Power feature to operate by storing messages destined for those nodes
Bearers¶
Mesh Profile specification allows two kinds of bearers for transmitting data:
Advertising Bearer
Uses LE advertising to broadcast messages to all nodes that are listening at this time
Uses non-connectable advertising only
29 octets of network message
GATT Bearer
Uses LE Connections to send messages
Uses standard GATT service (one for Provisioning and one for Proxy)
Provisioning¶
Provisioning is a process of adding an unprovisioned device to a mesh network managed by a Provisioner. A Provisioner provides the unprovisioned device with provisioning data that allows it to become a mesh node (network key, current IV index and unicast address). A Provisioner is typically a smart phone or other mobile computing device.
Models¶
Models define basic functionality of nodes on a mesh network. Mesh Profile Specification defines foundation models used to configure and manage network. Mesh Model Specification includes models defininig functionality that is standard across device types. Those consists of:
Generics - root models
On/Off
Level
Battery Server
Location
Client Property
and others
Sensors - defines a standard way of interfacing with sensors
Time and Scenes - defines a set of functionalities related to time and saved states on devices
Lighting - defines a set functionalities related to lighting control
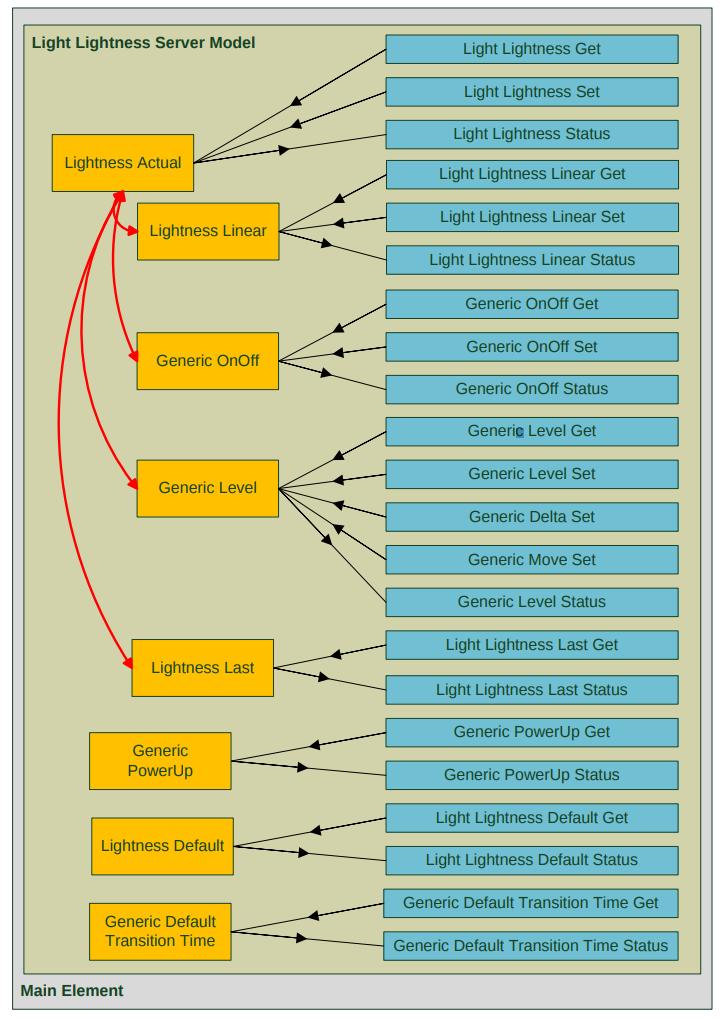
Complex models e.g. Lighting may contain other models eg Generic On/Off. The following image shows an example of Light Lightness Server Model.
Mesh Node features supported by Apache Mynewt¶
Advertising and GATT bearers
PB-GATT and PB-ADV provisioning
Foundation Models (server role)
Relay support
GATT Proxy
